Checking VPS/VDS Server Load
If your website is running slowly, it may be due to an increased server load.
The cause could be insufficient server resources allocated to your website or a potential attack on your site.
We will investigate and troubleshoot the cause of the increased load.
Using the «top» Command to Analyze Server Load
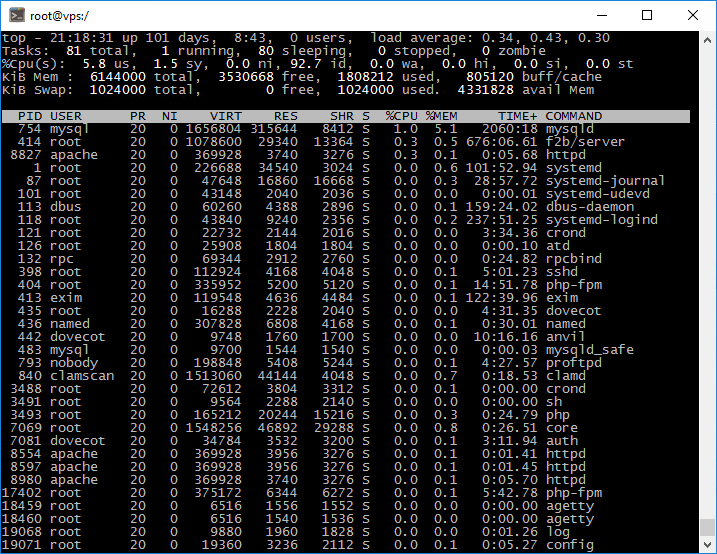
The «top» command is a primary tool for monitoring real-time server performance.
2. Once connected, type the command «top» and press Enter.
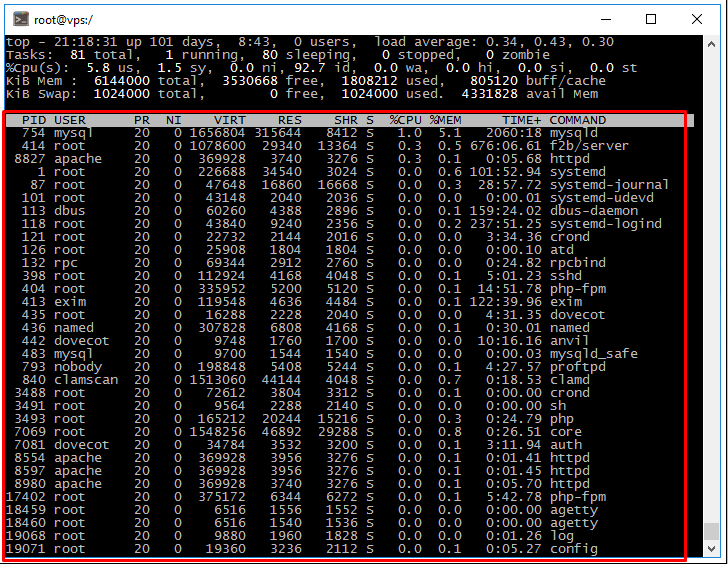
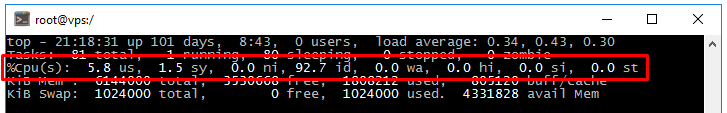
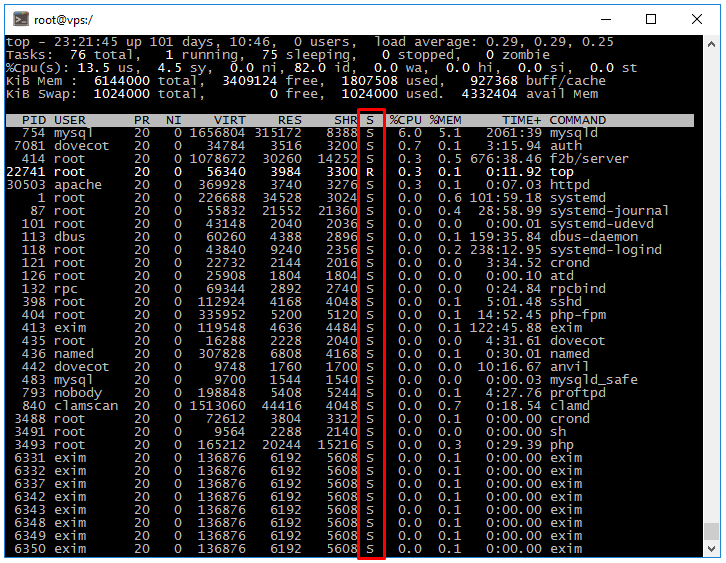
The program will display all running processes on your server in real time, allowing you to monitor server load and identify any resource-intensive processes. Resource usage information is displayed at the top of the screen. The list of running processes is displayed at the bottom. Let's analyze some of the key parameters displayed by the program.
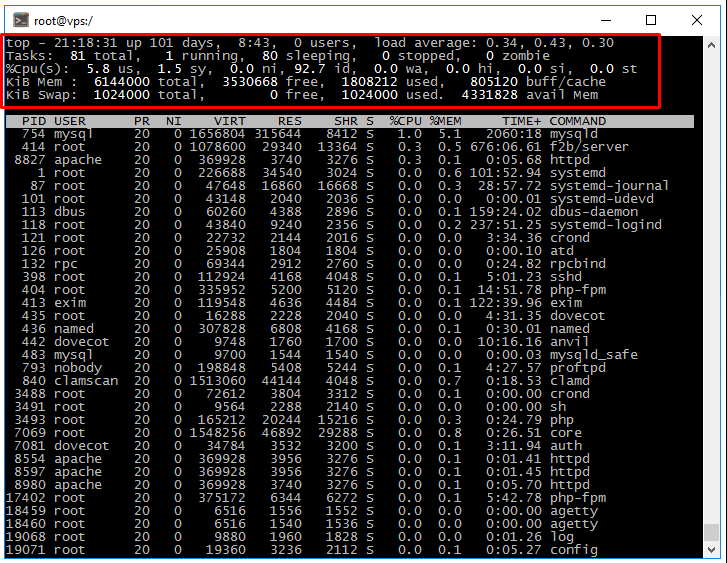
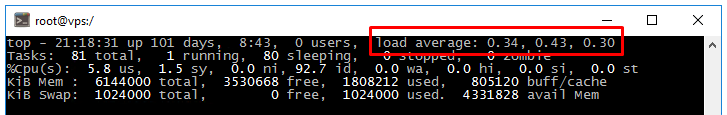
The average system load over a period of time is referred to as Load Average (LA).
It consists of three values representing the average load over the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes.
There are many conflicting opinions on what constitutes a «normal» load value. The load indicator is estimated by the number of cores in the system. A value of 0 is an idle core and 1 is a full core load.
CPU parameter.
The CPU line shows several load parameters at once:
- us (user) - CPU usage by user processes.
- sy (system) - CPU usage by system processes.
- ni (nice) - CPU usage by priority changed processes using the "nice" command.
- id (idle) - CPU idle is free resources.
- wa (IO-wait) - reports I/O related downtime
- hi (hardware interrupts) - indicates the CPU time used to service the hardware interrupt.
- si (software interrupts) - indicates the CPU time used to service the software interrupt.
- st (stolen by the hypervisor) - indicates the CPU time used by the hypervisor.
CPU load (parameters “sy”, “us”, “ni”).
By the %CPU column in the output of the "top" command, you can see the processes and make optimizations if necessary. Or just add CPU power to the server.
I/O load ("wa" parameter).
High "wa" values, as well as high LA, indicate idle processes in the D-state due to disk subsystem or network problems.
Simplified state model in Linux.
D-state is a continuous sleep state (processes waiting for an I/O thread to become free).
R-state is the process is currently active (currently running).
S-state is the waiting state (sleeping). It is waiting for some event or signal.
Ò-state is a process suspended by a STOP signal or by executing a trace.
Z-state is "zombie". A process that has terminated its execution but is present on the system to allow the parent process to read the exit code.
For a more detailed view, use the «ps aux» command.
Example: Investigating High «wa» and «Load Average» Issues
To find processes causing high «wa» (I/O wait) and Load Average, run the following command:
ps aux | grep D
This command displays processes in the D state (uninterruptible sleep), which typically indicates disk-related issues.